Understanding digital payments is crucial in today's fintech world. Two key terms you might encounter, especially within the realm of mobile wallets like Apple Pay and Google Pay, are DPAN (Device Primary Account Number) and MPAN (Merchant Primary Account Number).
These aren't just random acronyms; they represent sophisticated security measures designed to protect your sensitive credit and debit card information during transactions. This post will delve into what exactly a DPAN and an MPAN are, exploring their differences and highlighting why they are vital for secure digital payments.

What is a DPAN?
A DPAN (Device Primary Account Number) is a unique token assigned to a specific device when using Apple Pay. While it represents the cardholder's Primary Account Number (PAN), it doesn't expose actual card details. Each DPAN is tied to a single device—so the DPAN on your phone will differ from the one on your tablet, even if both are linked to the same card. This device-level distinction helps minimize risk, as a compromised token on one device won't affect others.
DPANs are issued by Apple Pay.
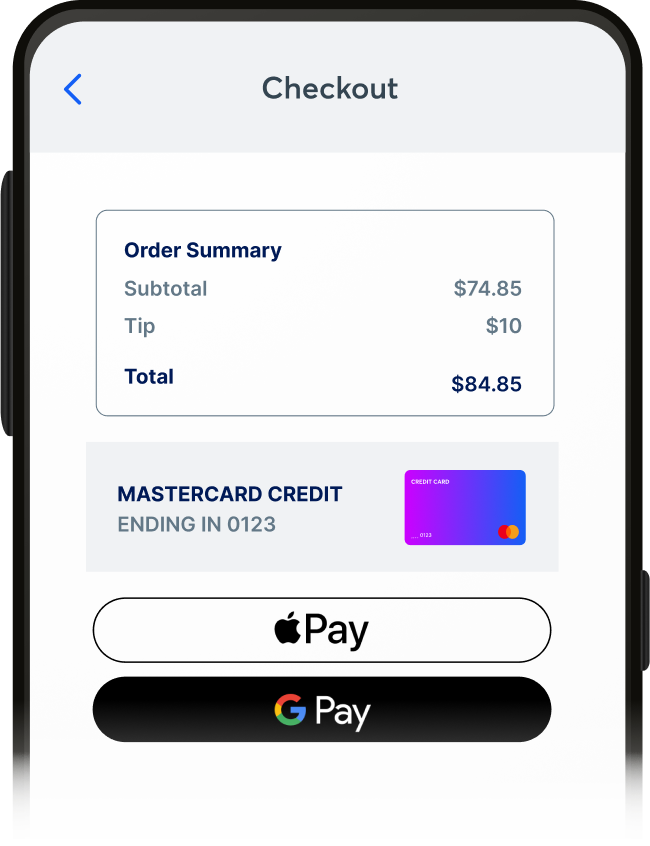
1
Add your card
A consumer adds their credit or debit card to Apple Pay on their phone.
2
Create a DPAN
Apple creates a unique card number, called the DPAN, for the device. This DPAN is linked to the consumer's card, but it's not the actual 16-digit PAN (Primary Account Number or better known as the customer's card number).
3
Make a payment
When a customer uses Apple Pay at checkout, the DPAN is sent to the merchant, not the card number.
4
Payment goes through
The payment processor recognizes the DPAN associated with the underlying card. The transaction is approved, and the payment is made.
5
Future payments
The DPAN is tied to the device, and is able to be used for future purchases, keeping the underlying card number safe and private. Keep in mind, this is applicable only for CIT transactions. MIT transactions will work for a short period until the network rules are enforced.
Enhanced Security: Since the DPAN is not a real card number, the real card number is never shared during transactions, reducing the risk of theft or fraud.
Privacy Protection: The real card details are kept private because only the DPAN is used for payments, making it harder for hackers to access the actual card information.
Tokenization: Each transaction uses a unique token (the DPAN), which makes it difficult for fraudsters to reuse the information from a previous payment.
Reduced Risk of Data Breaches: If a store or merchant is hacked, the attackers only get the DPAN, not the real card number, which limits the damage. Even if the DPAN is exposed, the hackers can't make a purchase as it requires the device the DPAN is associated with.
Easy Replacement: If a device is lost or stolen, the device owner can easily deactivate Apple Pay without needing to cancel the physical card, as the DPAN is tied to the device, not the physical card.
Convenience: Consumers don't need to carry your physical card around; the DPAN allows device users to make secure digital payments at checkout using their phone or watch, which is quick and easy.

What is a MPAN?
An MPAN (Merchant Primary Account Number) is a merchant-specific token linked to the user's iCloud account. This allows for continuity across devices but enhances security for recurring payments and provides better management for merchants.
MPANs are not issued by Apple Pay but rather in collaboration with the major networks (Visa, MasterCard, Discover, and AmEx). MPANs link the merchant, cardholder, and issuing bank together. This was done in a partnership with Apple and issuing banks to ensure Apple Pay is a trusted, secure digital wallet payment.
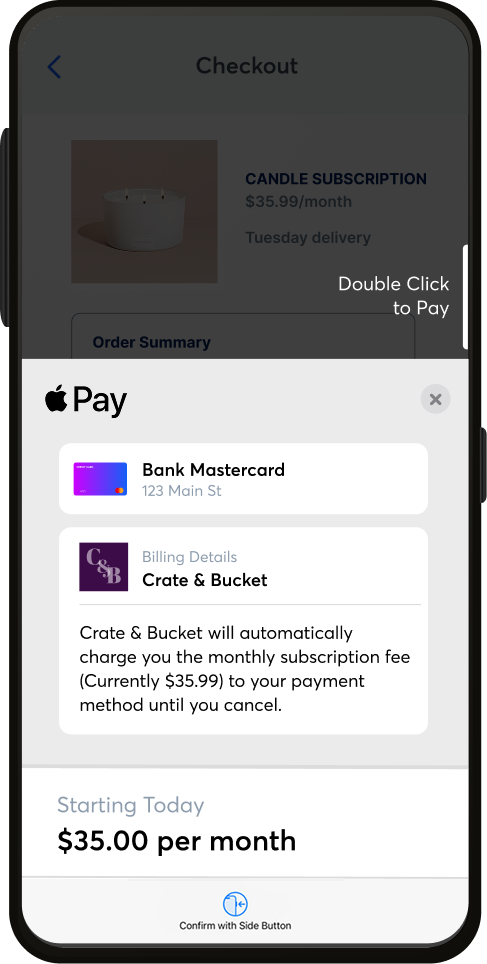
1
Customer Initiates Payment
When a customer makes a purchase with a merchant using Apple Pay, their device sends a payment request.
2
Token Generation
If an MPAN already exists for that card and merchant (e.g., for a recurring payment such as a subscription), it's used. If it's a new interaction or the issuer supports MPAN generation for the first time with this merchant, Apple Pay can request an MPAN.
3
Token Transmission
The MPAN is transmitted to the merchant's payment processor along with a one-time-use cryptogram for security.
4
Authorization
The payment processor sends the token and cryptogram to the payment network (e.g., Visa, Mastercard) where it is validated for approval or declined.
5
Future of Payments
MPAN can be easily used for recurring and repeat transactions for merchants
Secure Transactions: Apple Pay uses tokenization to replace sensitive payment details with unique merchant tokens. This helps protect both customers' and merchants' payment data during purchases and transactions.
Frictionless Payments: Merchants have a consistent identifier for a card across different devices of the same customer which is helpful for recurring payments.
Reduced Fraud Risk: Since Apple Pay uses the MPAN to identify and route transactions securely to the correct merchant, it ensures that only authorized transactions are processed, reducing the risk of fraud for businesses.
Device Flexibility: Consumers can pay with the same card seamlessly on all Apple devices with one MPAN.
Transparent Data: MPANs come with metadata DPANs do not allow for a more personalized purchase experience such as personalized notifications and detailed billing information after a recurring payment.
Seamless Lifecycle Updates: Unlike DPANs, MPANs help merchants access essential lifecycle management updates, enabling Apple Pay to automatically refresh and update stored payment methods for seamless transactions.

What is the difference between a DPAN and MPAN?
Understanding the distinction between DPANs and MPANs illuminates the sophisticated layers of protection built into modern digital payment systems, ensuring safer and more convenient transactions.
There are a few major differences to understand.
- Scope
While both are secure Apple Pay tokens used for digital payments, it's important to remember that DPANs are device specific, MPANs are merchant specific. - Portability
DPANs are device specific, tying them to one device only. MPANs are linked to the user's iCloud account so they can be used on any Apple device. - Device Specific
DPANs are device-specific and become invalid when a user switches to a new device. MPANs are not tied to a specific device, so they remain valid even when a user changes their device. - Use Case
DPANs are frequently used for one-time purchases or transactions while MPANs are better for recurring payments and transactions. - Issuing of Tokens
DPAN tokens are issued by Apple while MPANs are issued in collaboration with major networks.

What is the 'big' difference and which type of token is the preferred?
In essence, while both DPANs and MPANs are secure tokens replacing a user's PAN, MPANs offer greater flexibility and reliability, especially for recurring payments, by being tied to the merchant rather than a specific device. Apple is increasingly utilizing MPANs to improve the user experience and reduce payment failures in scenarios like subscriptions when users upgrade or change their Apple devices.
When asked what toke is preferred? Overall, MPANs offer significant security and benefits for digital payments.